Like it or not, electric-powered automobiles are on their way to replacing our current petrol and diesel rides.
Learning more about this developing technology is critical to thriving in this transition. We must equip ourselves with relevant knowledge to avoid falling behind.
The electric vehicle charger is one product of this growing industry that entails such attention—probably as much as learning and choosing your electric vehicle.
It only makes sense to familiarize ourselves with this piece of equipment. Like food is to people, this device is vital to an electric car’s existence.
What Exactly Is An EV Charger?
An EV charger is a device that replenishes an electric vehicle’s energy by connecting it to a source of electricity. In other words, it recharges an electric car by plugging it into a power supply.
While the term EV charger is pretty self-explanatory, we have to get more acquainted with some key aspects of this equipment.
One thing’s sure: You won’t get far with your electric vehicle without an electric vehicle charger (or EV charge point).
Getting To Know Your Equipment
Refuelling cars with internal combustion engines is quite simple. Customers go to a fuel station to supply their vehicle with either petrol or diesel. Filling up a tank takes only a few minutes.
On the other hand, figuring out which charge point to use can be challenging. You can’t just top-up in any station unless you have a compatible connector or appropriate cable.
Again, the technology is relatively new. We can safely attribute this difficulty to having limited knowledge about the apparatus. At the same time, these charge points have various specifications and configurations. They differ in capacity, charging time, and some other significant features.
However, once we learn the ropes, the whole charging process becomes less intimidating. Eventually, they can be second nature to us.
Read on to find out more about this next-level power-refilling device.

AC and DC Charge Points
Charge points can run on alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). Slow and fast chargers supply alternating currents. AC comes directly from the grid and is the available and standard current used in homes and establishments.
On the other hand, direct current flows straight to an EV’s battery from the power source or a charging hub through a rapid charger.
While some rapid chargers can also supply alternating current, this kind has declined for some time now.
Charging Speeds
There are different charger types involved in resupplying power to our vehicles. These types are classified based on charging speed dependent on the power output. The higher the power output, the faster a car is charged.
Mainly, there are slow, fast, and rapid chargers.

Rapid Charger
This charger is the fastest among the three types and supplies alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC).
Both AC and DC equipment can power up electric vehicles for up to 80% of their capacity in less than an hour. AC chargers are rated at 43kW, while the DC ones provide 50kW.
Fast Charger
This charge point can be found often in commercial locations, especially where people usually stay for an hour or more. Examples of these are parking areas and shopping centres.
Aside from public establishments, you can find fast chargers in workplaces, which is also the most common home charge point.
The rate at which they provide power ranges from 7kW to 22kW. The variation in power output also comes from the discrepancy in the recharge rate. Typically, the 22kW charger will restock power in three hours, while the 7kW will take twice as long.
Important Note: While 7kW and 22kW chargers promise fast charging rates, a car’s onboard charger also affects refuelling speeds. This process depends on the EV model’s capability to accommodate power outputs.
Even if you plug in with fast chargers, the EV dictates and controls the maximum capacity of power it can receive.
This limiter also protects your car from receiving more than it can manage.
Slow Charger
Charging with this equipment usually takes 6-12 hours as its power output is between 3kW to 6kW. They are generally used at home, though some workplaces and public spots also have these kinds of chargers.
Experts don’t recommend using this charger type unless drivers don’t have other means to top up. The high demand for electric current required to charge an EV makes this device unreliable for regular use.
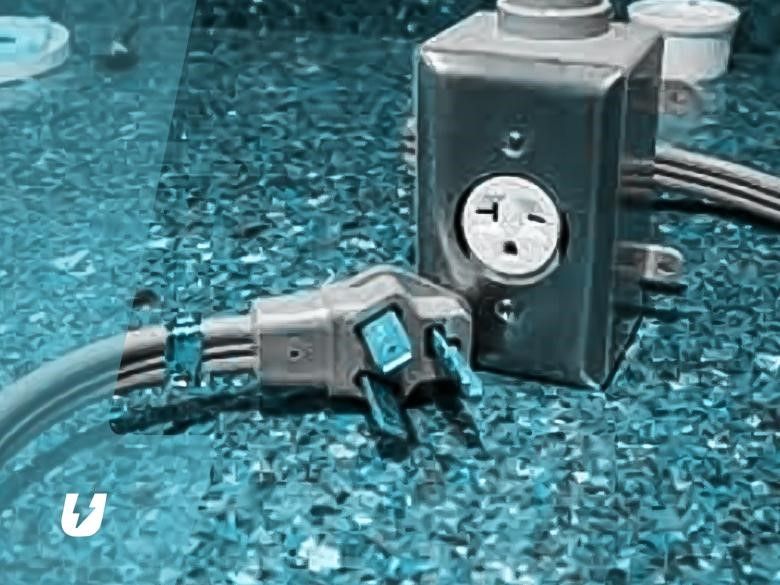

Hard-Wired Or Plug-In
There are two ways chargers connect to a power supply. There are plug-in charge points, and there are those that are hard-wired.
Hard-Wired
This charger is installed on your wall directly to a power supply. Compared to a plug-in, this one is more durable. It can withstand prolonged and repeated use. Its sturdy, weather-resistant cover makes it perfect for indoor and outdoor installation.
Because of the way it’s installed, hard-wired chargers have problems regarding mobility. However, this same issue is part of the reason it’s more secure. A stable installation is less prone to damage than one that can be easily moved around.
A hard-wired device will provide up to 40-amps of power for electric car charging at home.
Plug-In
This kind of charging is similar to how you power or charge your electrical devices. One end connects to the charging port while the other hooks up to your EV.
A 240-v plug is used for this unit and is much simpler to fit on walls. This unit is also much easier to relocate and move around. As long as there is an available 240-v outlet, it’s possible to replenish your car’s power.
With all its mobility, a plug-in charger has downsides. When supplying power, cars take longer to charge fully, with only 3.3kW hourly charging capacity.
Moreover, repeated plugging and unplugging give this device a shorter lifespan than its hard-wired counterpart.

Smart VS Dumb Chargers
EV chargers can be categorised into smart and dumb chargers. In a nutshell, smart chargers have more functions and can perform more specialised tasks than dumb chargers. Think of their difference as somewhat similar to a smartphone and an analogue phone.
Smart Chargers
Aside from their primary function of refilling an electric vehicle’s battery, smart chargers perform several other tasks that make the charging process more efficient. With smart chargers, EV users can monitor real-time charging, schedule charge sessions, set alarms or reminders, and even start or stop charging with a smart charger.
Dumb Chargers
This kind of charger does the main thing it was designed to do and intended for: resupply an electric car with power. Operating dumb chargers is uncomplicated, and some prefer their simplicity. These chargers have no other auxiliary tasks besides indicating kWh added and charge duration. This device will continue to supply power even if the battery is full.
The trade-off for this device is that a smart charger is expectedly more pricey due to its multiple features and functionalities.
Charger Locations
As more people convert to cleaner, zero (or low) emission driving resulting from switching to electric automobiles, the need to provide a reliable charging infrastructure also grew. Like petrol and diesel stations located anywhere in the country, charge point locations keep in step with this motoring revolution.
If you have an EV, here are the places you can go to keep your car running.
Public Places
You can often find these chargers in commercial locations such as parking areas, grocery and shopping establishments, gyms, cinemas, and any destination where customers stay for an extended period during the day.
Owners of such establishments recognise that their patrons and customers might need to recharge their EVs while they’re within their premises. Many use it as an incentive and offer charging services for free. 7kW charging is what’s commonly available in these locations.
Customers pay via contactless transactions when charging isn’t free, while some may require signing up or creating an account first.
Other public places where EVs can top up are motorways and service stations. EV drivers can do a quick top-up when necessary as they are on their way to their destination. You can find rapid chargers with tethered units in these stops.
Still, there are places where drivers can leave their cars for overnight charging. These can be found in or near hotels, perfect for travellers who need to recharge themselves and their EVs.

Workplace
Again, with the growing number of EV users comes the increased demand for charging facilities. The workplace is one other location where we can charge electric vehicles. While rapid chargers are mostly for fleet vehicles, employees and visitors have fast 7kW charging.
Homes
Many are ditching their internal combustion engine cars while adopting their own charging facility at home. Unlike petrol and diesel refuelling stations, home charger installation is possible due to the size of the charging equipment and the home’s capability to accommodate the relatively simple requirements of an electric car home charger.
Three-pin connectors make resupplying your EV battery at home possible. However, dedicated charge points are recommended for safer and faster charging.

Some Tips
Whether you already have an electric car or don’t have one yet, charging an electric car’s battery is arguably the second most important thing you need to consider upon switching to EV driving. Without power, EVs are essentially useless. Here are some things to consider when thinking about charging:
- Plan your trips. You must know the capabilities and range of your EV so that you’ll also know when and where you need to recharge your battery. There are many apps and websites that can help you find chargers along and in your destinations
- Know which type of connector is needed for your EV and make sure it’s compatible with the charging stations in your location. You can view the different types of EV charger connectors.
- Make sure that you only enlist the services of OZEV-approved installers for installations. Doing so will save you a lot of finances and trouble considering the job’s complexities and government restrictions and policies. Visit our website for more info about charge point installations.
- Look up the available government grants for EV purchases and charge point installations. These subsidies can help minimise costs from your end.
Government Grants
Believe it or not, the UK government, through the Office For Zero Emission Vehicles (OZEV) is assisting private individuals, businesses, charity organisations, and local authorities to switch to EV driving through various grants.
There is the Electric Vehicle Chargepoint Grant which replaced Electric Vehicles Homecharge Scheme (EVHS) in April 2022. There is also the Workplace Charging Scheme (WCS), On-street Residential Chargepoint Scheme (ORCS), and the Plug-In Car Grant (PICG). These grants cover a portion of the cost when buying an electric car and purchasing and installing a charge point.
Why is this important? For those who have questions regarding the cost of acquiring chargers and EVs, considering these grants in our calculations can help better answer the issue of expenditures.
The following are recent updates to the different government grants. They mainly involve the WCS and EVHS:
- The Electric Vehicle Chargepoint Grant offers a £350 grant. However, unlike the EVHS, which is open for homeowners, the grant is limited to landlords, social housing providers, and those living in rental accommodations
- The WCS will be open to charities, SME’s, and B&B’s/
You can find the complete OZEV Grant updates on the official government website.
What Happens Now?
Having used fossil fuel cars for so long, switching to EVs equates to a lifestyle change. We’d have to embrace new habits associated with driving these newer automobiles. And yes, this includes how we refuel—or in this case, recharge—our e-vehicles.
The importance of this piece of equipment cannot be over-emphasised—these are the refuelling stations of the future.
The eco-friendly, sustainable, and cleaner electric driving revolution is happening fast. As more of these vehicles find their way onto our streets, so will EV chargers. Don’t let yourself get left behind! Contact us, and we’ll gladly help you have that EV charger installed at home or work!
Want to become an expert on the subject? Learn more by clicking here: Best Home EV Charger UK